Comprehensive Insights into Mesothelioma
Mesothelioma is a rare and aggressive cancer that primarily affects the mesothelium, a protective lining that covers many internal organs. This article delves into the types of mesothelioma, its causes, symptoms, diagnosis, treatment options, and support for those affected.
Understanding Mesothelioma
What is Mesothelioma?
Mesothelioma is a type of cancer that arises from the mesothelial cells of the mesothelium, which lines the lungs, abdomen, heart, and other organs. The most common type of mesothelioma is pleural mesothelioma, which affects the lungs. Other types include peritoneal mesothelioma (affecting the abdomen), pericardial mesothelioma (affecting the heart), and testicular mesothelioma.
Types of Mesothelioma
- Pleural Mesothelioma:
- This is the most prevalent form, accounting for approximately 75% of all cases. It develops in the pleura, the lining of the lungs and chest cavity.
- Peritoneal Mesothelioma:
- This type occurs in the peritoneum, the lining of the abdominal cavity. It represents about 20% of mesothelioma cases.
- Pericardial Mesothelioma:
- A rare form affecting the lining around the heart, it constitutes a small percentage of mesothelioma cases.
- Testicular Mesothelioma:
- This is the rarest form and affects the tunica vaginalis, the lining surrounding the testicles.
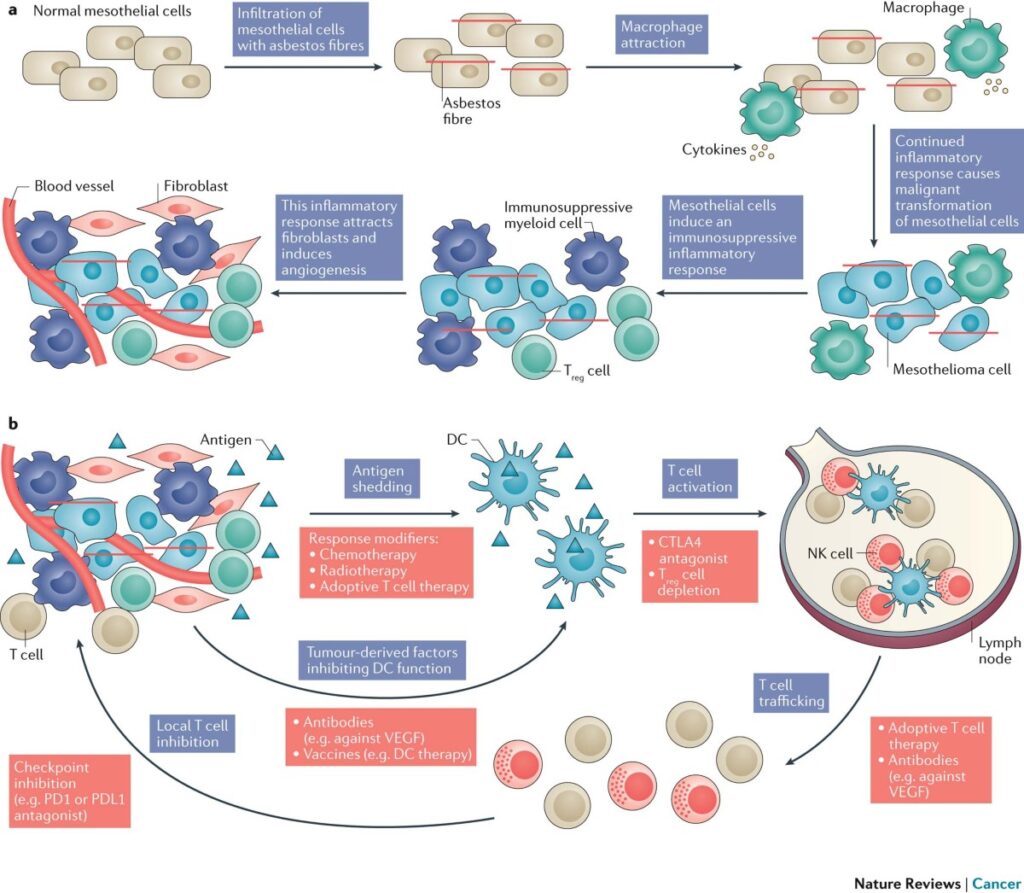
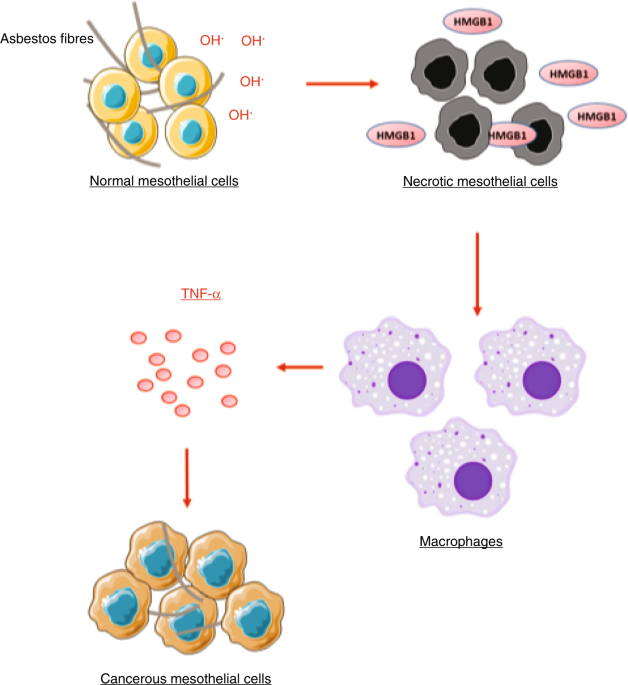
Causes and Risk Factors
Asbestos Exposure
The primary cause of mesothelioma is exposure to asbestos, a naturally occurring mineral that was widely used in construction, insulation, and manufacturing due to its fire-resistant properties. When asbestos fibers are inhaled or ingested, they can become trapped in the mesothelium, leading to inflammation and eventually cancer.
Other Risk Factors
While asbestos exposure is the leading cause, other risk factors include:
- Genetic Factors: Some individuals may have a genetic predisposition to mesothelioma.
- Radiation Exposure: Individuals who have undergone radiation therapy for other cancers may be at increased risk.
- Age and Gender: Mesothelioma is more common in older adults, typically occurring in those over 65, and is more prevalent in men than women.
Symptoms of Mesothelioma
Early Symptoms
Symptoms of mesothelioma often do not appear until decades after exposure to asbestos, making early detection challenging. Common early symptoms may include:
- Persistent cough
- Shortness of breath
- Chest pain or discomfort
- Fatigue
- Unexplained weight loss
Advanced Symptoms
As the disease progresses, more severe symptoms may arise, such as:
- Severe respiratory difficulties
- Swelling in the abdomen or chest
- Night sweats or fever
- Difficulty swallowing
- Neurological symptoms in cases of advanced disease
Diagnosis
Medical Evaluation
Diagnosing mesothelioma begins with a comprehensive medical evaluation, including:
- Medical History: A thorough review of the patient’s exposure to asbestos and any family history of cancer.
- Physical Examination: Checking for signs of fluid accumulation, lung function, and general health.
Imaging Tests
Doctors often use imaging tests to identify abnormalities in the chest or abdomen. Common imaging tests include:
- X-rays: Can reveal fluid buildup or masses in the lungs.
- CT Scans: Provide detailed cross-sectional images of the body, helping to locate tumors.
- MRI Scans: Useful for assessing the spread of cancer to surrounding tissues.
Biopsy
A definitive diagnosis of mesothelioma requires a biopsy, where a tissue sample is taken from the affected area for microscopic examination. Various biopsy methods include:
- Needle Biopsy: A thin needle is used to extract tissue.
- Thoracoscopy: A minimally invasive procedure to view the chest cavity and take samples.
- Laparoscopy: A surgical procedure for abdominal biopsy.
Treatment Options
Surgery
Surgery may be an option for early-stage mesothelioma, aiming to remove tumors and affected tissue. Common surgical procedures include:
- Pleurectomy/Decortication (P/D): Removing the pleura and visible tumors.
- Extrapleural Pneumonectomy (EPP): Removing an entire lung, pleura, and nearby tissues.
Chemotherapy
Chemotherapy uses drugs to kill cancer cells and is often employed in conjunction with surgery. Common chemotherapy regimens for mesothelioma may include:
- Cisplatin and Pemetrexed: Standard combination therapy for pleural mesothelioma.
Radiation Therapy
Radiation therapy utilizes high-energy rays to target and kill cancer cells. It can be used after surgery to eliminate remaining cancer cells or as palliative treatment to alleviate symptoms.
Immunotherapy
Immunotherapy leverages the body’s immune system to fight cancer. Emerging treatments, such as checkpoint inhibitors, are being studied for mesothelioma treatment.
Clinical Trials
Participating in clinical trials can provide access to cutting-edge treatments and therapies that are not yet widely available. Patients should discuss with their healthcare team to explore ongoing clinical trials.
Prognosis
Factors Influencing Prognosis
The prognosis for mesothelioma varies based on several factors, including:
- Type and Stage of Cancer: Early-stage mesothelioma generally has a better prognosis than advanced stages.
- Patient’s Age and Overall Health: Younger, healthier patients may respond better to treatment.
- Response to Treatment: Individual responses to therapies can significantly impact outcomes.
Survival Rates
Survival rates for mesothelioma are generally low due to late diagnosis and aggressive nature. The median survival time for pleural mesothelioma ranges from 12 to 21 months post-diagnosis, with some patients living longer depending on treatment and individual factors.
Support and Resources
Support for Patients and Families
Coping with a mesothelioma diagnosis can be challenging for patients and their families. Support resources include:
- Support Groups: Connecting with others facing similar challenges can provide emotional support.
- Counseling Services: Professional counseling can help address mental health needs.
- Palliative Care: Focused on improving the quality of life, palliative care can provide relief from symptoms.
Legal and Financial Assistance
Due to the link between mesothelioma and asbestos exposure, many patients pursue legal action against responsible parties. Legal resources and financial assistance programs are available to help with medical expenses and provide compensation for damages.
Conclusion
Mesothelioma is a complex and devastating disease primarily caused by asbestos exposure. Early detection is critical for improving outcomes, but the aggressive nature of the disease often complicates this. A multi-disciplinary approach to treatment, including surgery, chemotherapy, and emerging therapies, can help manage the disease and improve quality of life. Support resources are vital for patients and families navigating the challenges posed by mesothelioma. By raising awareness and providing education about this disease, we can empower those affected and foster a community of support and understanding.